Ampere's Circuital Law
Ampere's Circuital Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Ampere's Circuital Law, Amperian Loops for Various Current Carrying Objects, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Wire Using Ampere's Law, Similarity between Gauss's Theorem and Ampere's Circuital Law, Toroid, etc.
Important Questions on Ampere's Circuital Law
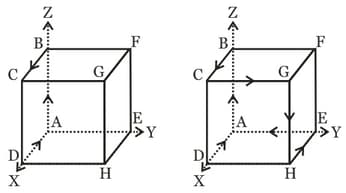
Current I is following along the path ABCD, along the four edges of the cube (figure-a) creates a magnetic field in the centre of the cube of . Find the magnetic field B created at the centre of the cube current I following along the path of the six edges ABCDHEA figure - b
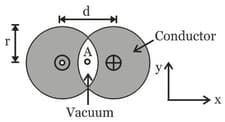
Two long conductors are arranged as shown above to form overlapping cylinders, each of radius r, whose centres are separated by a distance d. Current of density J flows into the plane of the page along the shaded part of one conductor and an equal current flows out of the plane of the page along the shaded portion of the other, as shown. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point A ?
infinitely long thin wires each carrying current in the same direction, are in the plane in a gravity-free space. The central wire is along the -axis while the other two are along with If the central wire is displaced along the -direction by a small amount & released, the wire executes the simple harmonic motion. If the linear density of the wire is , find the frequency of oscillation.
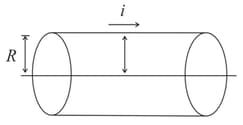
A cylindrical conductor of radius carries a current along its length. The current density , however, is not uniform over the cross-section of the conductor but is a function of the radius according to , where is a constant. Then the expression for the magnetic field
at
at
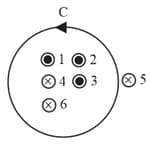
Six wires of current and cut the page perpendicularly at the points and respectively as shown in the figure. Find the value of integral around the circular path
If a magnetic field exists in space then the plane through which magnetic flux will be zero is
Two concentric and coplanar circular loops P and Q have their radii in the ratio . Loop Q carries a current in the anticlockwise direction. For the magnetic field to be zero at the common centre, loop P must carry
A closed curve encircles several conductors.The line integral around this curve is . What is the net current in the conductors?
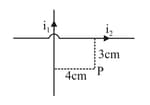
Two insulated wires of infinite length are lying mutually at right angles to each other as shown in. Currents of and respectively are flowing in them. The value of magnetic induction at point P will be-
Only the current inside the amperian loop contributes in
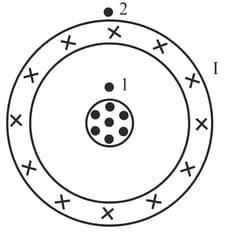
The figure shows the cross-section of two long co-axial tubes carrying equal current in opposite direction at point 1 and 2, as shown in the figure then
A closed curve encircles several conductors. The line integral around this curve is . What is the net current in the conductors?
A closed curve encircles several conductors. The line integral around this curve is . What is the net current in the conductors?
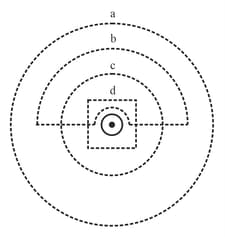
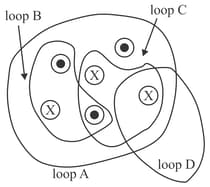
Rank the magnitudes of for the closed paths in figure, from least to greatest.
A toroid has a core (non-ferro magnetic) of inner radius and outer radius around which turns of a wire is wound. If the current in the wire is , the magnetic field inside the core of the toroid is
A toroid has a non ferromagnetic core of inner radius and outer radius , around which turns of a wire are wound. If the current in the wire is , the magnetic field inside the core of the toroid is
Similar or same magnetic fields can be produced by
Four wires carrying current and respectively cut the page perpendicularly as shown in figure. The value of for the loop shown would be:
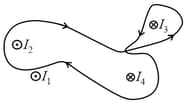
Consider six wires coming into or out of the page, all with the same current. Rank the line integral of the magnetic field (from most positive to most negative) taken counterclockwise around each loop shown.
The relative permeability in a core of a solenoid is . The windings of a solenoid are insulated from the core and carry a current of . If the number of turns is per meter. Then magnetic intensity inside the core of solenoid is _____
